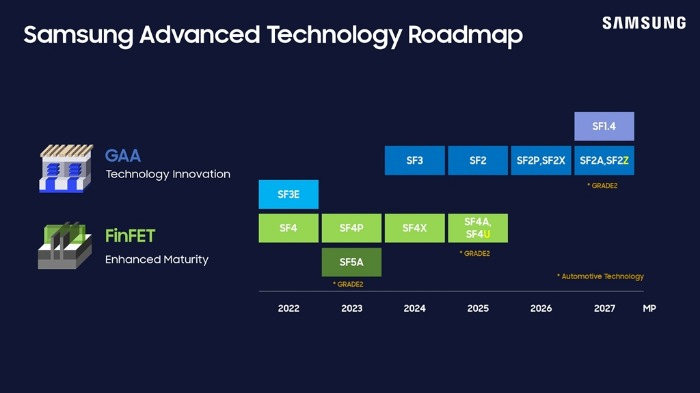
A new contract chipmaking technology, dubbed the backside power delivery network (BSPDN), will reduce the size of a 2-nanometer chip by 17%, compared with the traditional front-end power delivery technology, said Samsung Electronics Co.'s foundry business executive on Thursday.
The BSPDN, which Samsung is set to apply for mass production of the 2 nm process from 2027, also improves performance and power efficiency by 8% and 15%, respectively, compared to the chips with the front-end power delivery networks, said Lee Sungjae, vice president and Foundry PDK Development Team at Samsung.
He outlined the technological prowess of BSPDN in a keynote speech at Siemens EDA Forum 2024. It was the first time for a Samsung foundry business executive to give a detailed account of its BSPDN technology in public.
BSPDN is called a next-generation chip foundry technology. It places power rails on the back of the semiconductor wafer to eliminate bottlenecks between the power and signal lines, allowing for smaller chips.
Contract chipmakers are gearing up to adopt the advanced chipmaking process. Leading the pack, Intel plans to produce chips with BSPDN on the Intel 20A process, known as a 2 nm node, within the year. It dubbed its BSPDN technology as PowerVia.
TSMC, which controls 62% of the global foundry market, said it plans to introduce the BSPDN to its 1.6 nm and below process nodes around the end of 2026.
Lee also unveiled the roadmap and performance of chips to be made with the next-generation gate-all-around (GAA) technology that Samsung adopted in 2022 for the first time in the world.
It plans to mass-produce 3 nm chips based on the second-generation GAA technology (SF3) in the second half of this year and deliver GAA on its upcoming 2 nm process.
SF3 has improved chip performance and power efficiency by 30% and 50%, respectively, while reducing the chip size by 35%, compared with the chips produced on the first-generation GAA process, Lee added.
Abonnieren fuer regelmaessige Marktupdates.
Bleiben Sie auf dem neuesten Stand der Branchentrends, indem Sie unseren Newsletter abonnieren. Unser Newsletter ist Ihr Zugang zu erstklassiger Marktexpertise.
ChangXin Memory Technologies (CXMT), China's top DRAM supplier, is reportedly preparing to phase out DDR4 products for server and PC use by mid-2026. As the company pivots to DDR5 and high-bandwid

Japan's push to revive its semiconductor manufacturing is hitting speed bumps as major manufacturers expressed cautiousness over operation or expansion amid weak demand outside of AI.According to
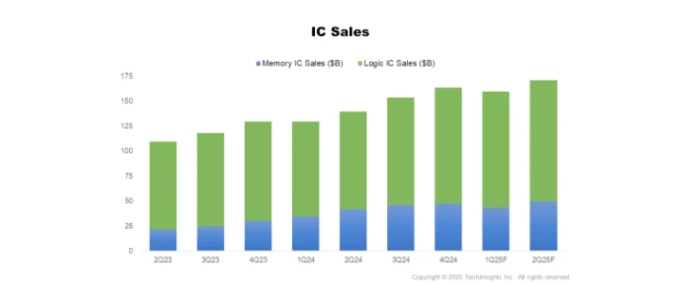
The global semiconductor manufacturing industry entered 2025 with typical seasonal patterns. However, looming tariff threats and evolving supply chain strategies are expected to create atypical season

At the TSMC Technology Symposium 2025 on May 15 in Hsinchu, Taiwan, T.S. Chang, VP of Advanced Technology and Mask Engineering at TSMC, announced the company's accelerated fab expansion plans. Pre
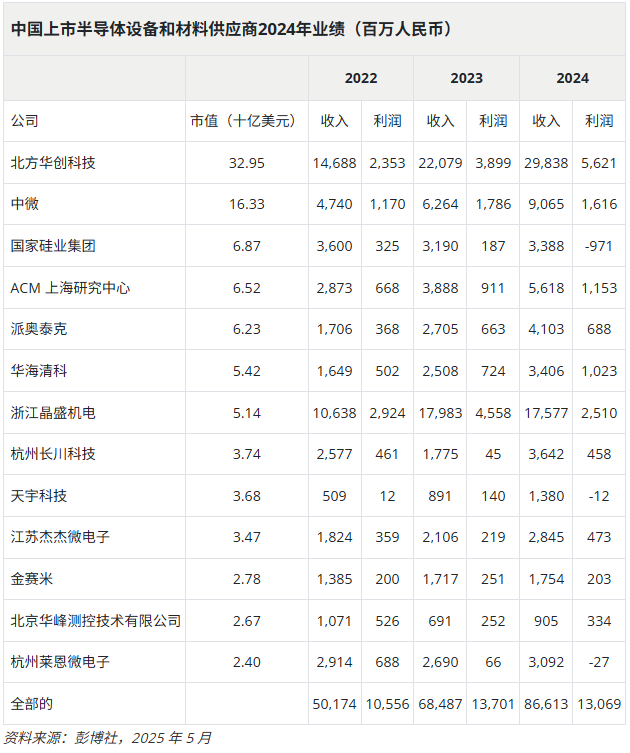
Chinese listed semiconductor equipment and materials companies released their 2024 annual financial reports in late April, revealing strong revenue growth but a decline in overall profitability. Despi
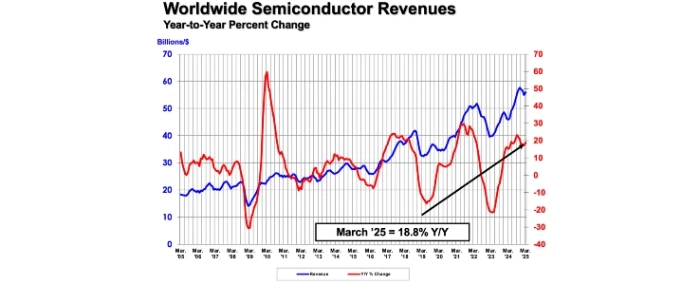
The Semiconductor Industry Association (SIA) reports that global semiconductor sales reached USD 167.7 billion in the first quarter of 2025, marking an 18.8% increase compared to the same period last